Share
In the healthcare industry, manual handling is a high-risk activity that involves physically moving and supporting patients. Managing the risks of manual handling is crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of healthcare workers and patients alike.
Here, we’ll provide comprehensive information about Safe Work Australia (WorkSafe) manual handling principles in patient care, including examples of manual handling hazards and strategies to mitigate these risks.
EXAMPLES OF MANUAL HANDLING HAZARDS IN PATIENT CARE
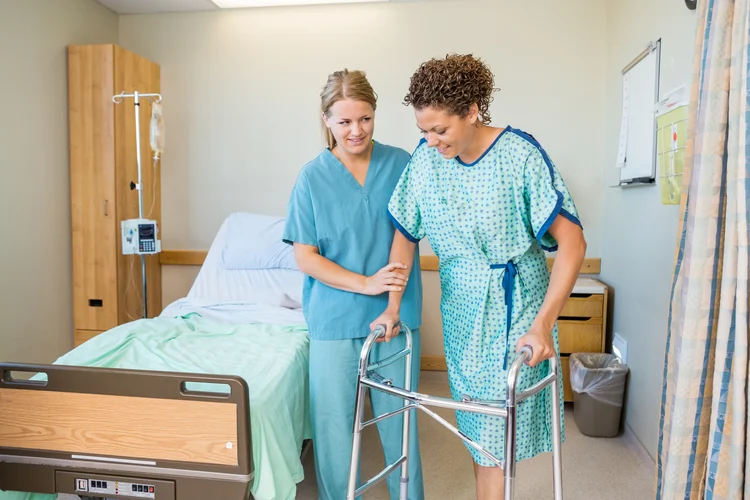

Manual handling tasks in healthcare settings can pose significant risks to workers. Examples of manual handling hazards include:
- Heavy lifting: Healthcare workers may have to manually lift and move patients, which can strain their muscles and lead to musculoskeletal injuries.
- Awkward postures: Patient care tasks often involve bending, twisting, or reaching in awkward positions, which can increase the risk of strains and sprains.
- Repetitive motions: Performing repetitive manual handling tasks, like transferring patients, can lead to overexertion injuries and musculoskeletal disorders.
- Insufficient staffing: A lack of adequate staff can result in healthcare workers handling patients independently, increasing the risk of injuries due to fatigue or improper lifting techniques.
- Patient weight: Bariatric patients can make manual handling tasks more challenging and increase the risk of injuries for healthcare workers.
- Lack of training: Insufficient training in proper lifting and handling techniques can increase the likelihood of accidents and injuries during patient care activities.
- Inadequate equipment: The absence or improper use of assistive patient handling equipment, like patient transfer and lifting devices, can contribute to manual handling hazards.
- Environmental factors: Patient handling tasks in areas with limited space, slippery floors, or obstacles can increase the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Psychosocial factors: Patient care activities can be physically and emotionally demanding, leading to increased stress levels and the potential for psychological strain on healthcare workers.
- Lack of communication and teamwork: Inadequate communication and coordination among team members during manual handling tasks can increase the risk of accidents and injuries.
To effectively manage these manual handling examples, it’s essential to adopt a systematic approach. This involves identifying hazards, assessing risks, implementing control measures, and regularly reviewing and monitoring the effectiveness of these measures.
WORKSAFE MANUAL HANDLING ROLES

Work health and safety, including manual handling, is governed by regulations and guidelines to ensure the well-being of healthcare workers. The Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Act and the Model OHS Regulations outline the responsibilities of employers, employees, and other duty holders in managing manual handling risks.
EMPLOYER’S DUTIES
Employers have specific duties to provide a safe working environment for their employees. These duties include:
- Ensuring a Safe Working Environment: Employers must maintain a workplace free from risks to health and safety, including hazards associated with manual handling.
- Information, Instruction, and Training: Employers should provide employees with the necessary information, instruction, training, and supervision to enable them to perform their work safely without risks to their health.
- Preventing Endangerment: Employers must ensure that their business activities do not endanger the health and safety of others, including visitors, the public, and other workers.
EMPLOYEE’S DUTIES
Employees also have responsibilities to ensure their own health and safety, as well as the safety of others. These duties include:
- Taking Reasonable Care: Employees must take reasonable care of their own health and safety and that of others who may be affected by their actions or omissions in the workplace.
- Cooperating with Employers: Employees should cooperate with their employers in complying with the OHS Act and Regulations, following safe work policies and procedures, and attending relevant training.
IDENTIFYING, ASSESSING & CONTROLLING MANUAL HANDLING HAZARDS
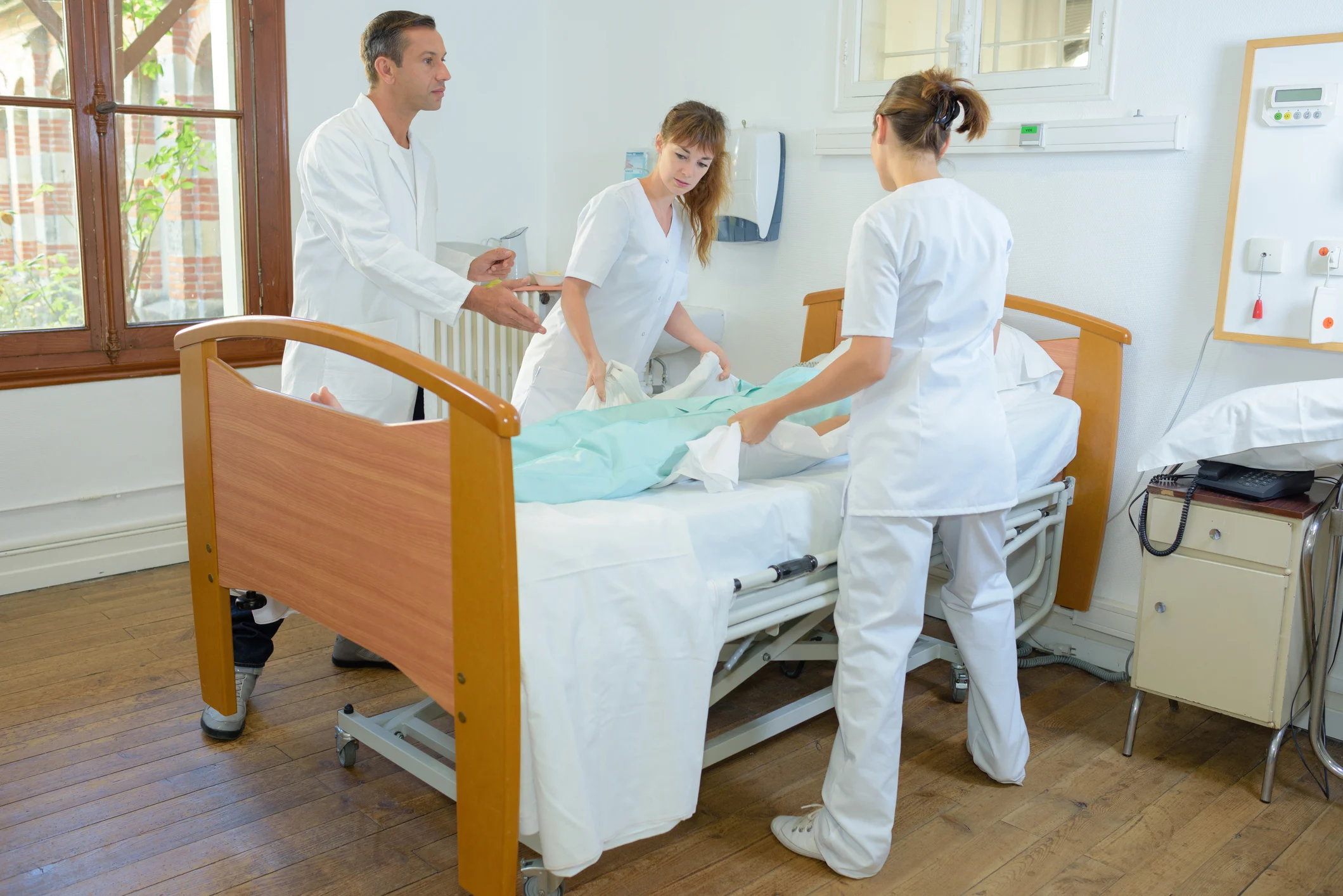

The first step in managing manual handling risks is to identify potential hazards. This can be done through risk assessments and consultations with workers. Employees directly involved in manual handling tasks can provide valuable insights into the hazards present in their work.
Consideration should be given to factors such as patients' physical characteristics (weight, size, strength), their state of consciousness, unpredictable behaviour, willingness to assist, and ability to communicate and understand instructions.
ONCE MANUAL HANDLING OHS HAZARDS HAVE BEEN IDENTIFIED
A thorough risk assessment should be conducted to evaluate the risk associated with each manual handling task. The risk assessment should consider postures, movements, and forces that may pose a risk and the circumstances where these risks become dangerous.
Control measures should be implemented to eliminate or minimise the identified risks. This might include:
- Mobility Risk Assessment: Maximising the patient's ability to assist during manual handling tasks through appropriate advice, mechanical aids, and assistive devices.
- Optimising Work Area: Ensuring the work area allows for safe and unrestricted movement during manual handling tasks. This may involve using specialised equipment like transfer benches or adjustable beds to facilitate patient care activities.
- Task Planning: Assessing the specific needs of each manual handling task and planning it to minimise the risk. This may involve using mechanical aids or additional personnel to share the load.
- Ceiling Hoists: Utilising ceiling hoists for patient transfers, ensuring proper training and supervision are provided when using this equipment.
- Training: Providing comprehensive training on the safe use of mechanical aids and assistive devices to healthcare workers involved in manual handling tasks.
MONITORING & REVIEWS
Regular monitoring and review are crucial to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of control measures. This involves evaluating the implemented control measures, identifying any new hazards or changes in the work environment, and making necessary adjustments to the risk management strategies.
Workplaces should foster a culture of continuous improvement and encourage employee feedback regarding the effectiveness of control measures. This feedback can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that manual handling risks are consistently managed.
WORKSAFE MANUAL HANDLING PRINCIPLES PLAY A VITAL ROLE IN ENSURING THE SAFETY AND WELL-BEING OF HEALTHCARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS
By identifying hazards, assessing risks, and implementing control measures, healthcare organisations can minimise the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and create a safer working environment.
It is essential for employers and employees to understand their respective duties and responsibilities in managing manual handling risks. Working together and following best practices, healthcare organisations can prioritise the health and safety of their workers while providing high-quality patient care.
Active Mobility stocks a range of manual handling products and equipment to reduce the risk of injuries and discomfort in healthcare workers and patients. Shop the range online!